With liquidity in excess of K3.3bln into Thursday 18 June treasury bill sale, the central bank in Africa’s second largest copper producer sold K2bln worth of government securities. Appetite observed was in excess of K3.3bln of which 61.2% was absorbed with K1.3bln housed in the 1year tenor paying 28.0%. This is the fifth oversubscription with the Bank of Zambia borrowing over and above its 40% threshold.
Funding costs climbing down? Yields rallied 75bps to 28.0% in the 1year while the 3months decreased 50bps to 17.0% as the other tenors namely 6months and 9months climbed down 25bps and 33bps respectively. This rally for the long end is 125bps from 29.2501% levels on April 23 the week before the central bank stimulus package was announced.
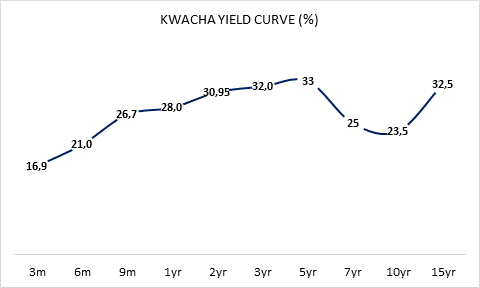
Analysts forecast a yield curve ‘climb down’ from the elevated levels exacerbated by fiscal posture. The 100bps margin above the benchmark interest rate was dubbed by most market analysts as cheap pricing that would allow for commercial banks to reprice their funding costs and balance sheets by accessing the K10bln credit line but for the prohibitive requirements such as steep haircuts on collateral and size of performing books which has resulted in some inertia in the easing of yields downwards. Average Lending Rates – ALR have eased 81bps in the May to 27.94% from 28.75% in March.
Risk skew – shorter dated higher yielding assets. With elevated fiscal risks amplified by COVID effects, it is evident that Zambia could not be receiving assistance from the IMF any time soon until debt reorganization is ticked off, uncertainty is clearly priced in the premiums and as such players prefer shorter dated to fixed income (>1yr paper) bonds. Zambia has 14 months to elections and political risk is priced into the shorter dated risk appetite skew. There is a good chance Zambia could restructure Chinese debt within a 6month period which could offer reprieve and latitude to service the $750mln 2022 maturity.
The central banks have continued to fund Open Market Operations – OMOs circa one and half yards monthly leaving the markets fairly liquid.
Zambia’s recession forecast as revised lower to -0.8% by the World bank from -2.6% earlier in April at the virtual spring meetings.
The Kwacha Arbitrageur

